Liver Man of India: Dr S K Sarin
Meeting world fame gastroenterologist Dr S K.Sarin at Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), New Delhi was an uplifting experience that filled Double Helical Team with inherently positive vibes and immensely feel-good factor…….
During an hour-long conversation with him, he dwelt at length on the benefits of healthy liver which by harmonizing our inherent natural life-force helps to eliminate sickness and restore positive health and total wellness.
With outstanding contribution and top notch performance in medical education, Dr Sarin is well known as top gastroenterologist, hepatologist, a pioneer in clinical innovations, a gifted teacher, and a hybrid with great insights into basic and clinical research. Today no amount of appreciation can do justice with his talent, goodness, generosity, greatness and kindness. At present he is working as Chancellor and Director at the Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), the first of its kind in Asia. ILBS is the first, cost-effective and most comprehensive Liver Set-up in the region.
 Dr Sarin approach for primary prevention of variceal bleeding by band ligation has become the standard of care worldwide. Similarly, the management protocols on Gastric Varices; and the nomenclature bearing his name as ‘Sarin’s Classification of Gastric Varices” are universally followed. He has more than 350 International publications to his credit, including The New England Journal of Medicine, The Lancet, Annals of Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Dr Sarin approach for primary prevention of variceal bleeding by band ligation has become the standard of care worldwide. Similarly, the management protocols on Gastric Varices; and the nomenclature bearing his name as ‘Sarin’s Classification of Gastric Varices” are universally followed. He has more than 350 International publications to his credit, including The New England Journal of Medicine, The Lancet, Annals of Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
His deep interest in physiology has recently resulted in the development of a unique model of endotoxemia induced portal hypertension and liver disease. He has helped describe two new disease entities, portal biliopathy, and ‘Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure”.
Dr Sarin is credited globally to give a huge number relevant and new protocol for the management of patients with hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver and its complications. His recent contributions in the field of liver regeneration using growth factors has a great potential for patients with advanced liver disease and liver failure so as to provide options of transplant free survival. His outstanding contribution to develop 17 major treatment guidelines, including spearheading five major Asian Pacific Treatment Guidelines in Liver diseases; are being widely quoted and practiced.
He has also immensely contributed to the field of hepatitis B, C and liver cancer. He is instrumental in changing the nomenclature of ‘Hepatitis B carrier’ to “Chronic HBV Infection”. The treatment options and pathogenesis of these diseases have been greatly advanced by his work. He is deeply involved in preventing and protecting new born babies from HBV transmission. His group showed that the mother baby transmission is the major route of transmission of hepatitis B in India. He also showed for the first time that the newborns born to these mothers are already chronically infected with HBV. The treatment of hepatitis B and C, alcoholic liver disease and liver cancer are specially looked after by him.
Along with the team of experts from Asia, he has been able to define a new disease entity, Acute on Chronic Liver Failure (ACLF). Since such patients have a high mortality, the need for protocol based treatment and special intensive care management has been established through his efforts. This has led to improved outcomes by their team
 Prof. Sarin, with his intense dedication, vision and work, is a role model for the country. He has been bestowed with Padma Bhushan by the Govt of India. He is also the recipient of several other awards, apart from this he is one of the most sought teachers, invited speaker nationally and internationally, and has been awarded the “Gifted Teacher Award” by the Association of Physicians of India.
Prof. Sarin, with his intense dedication, vision and work, is a role model for the country. He has been bestowed with Padma Bhushan by the Govt of India. He is also the recipient of several other awards, apart from this he is one of the most sought teachers, invited speaker nationally and internationally, and has been awarded the “Gifted Teacher Award” by the Association of Physicians of India.
According to Dr S K Sarin, the problem of liver disease was always there. Even in 2000 BC there were no worship of god and goddess in the temples. The liver was only kept. There was great importance of liver in Babylonians times. Because people knew that liver is the centre of the body. Heart was only discovered 400 to 500 years ago. Liver is sheet of your body as pillar. This is also largest and very tolerant organ of the body. So if you are not careful about your liver than it becomes worse. Lot of times what you eat and what you drink, liver can tolerate but after a while it revolts.
Today common causes of liver disease are obesity, overweight, excess fat, alcohol and no knowledge of Hepatitis B and C virus. Non judicious of use of drugs is also one of the causes of liver disease. Liver carries out over 500 tasks and plays an essential role in digestion. Its roles include detoxification, protein synthesis, and producing digestive enzymes. The roles of the liver include detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of chemicals that help digest food. It is part of the digestive system.
 Role of Liver
Role of Liver
Liver is as a solid organ, located in the right upper part of the abdomen just below the rib cage. It is a complex organ both structurally and functionally. Liver is a pivotal organ for metabolic functions of our body. The function of liver can be categorized into two major groups: excretory function and synthetic function. Most foreign substances and waste product made in body are metabolized within the liver before being excreted via bile or kidney. Excretion of bilirubin from liver is important as defect in bilirubin excretion leads to jaundice. Liver is the site of synthesis of all major proteins in body. These proteins are building blocks for all important functions in body. Bile is synthesized in liver and which helps in digestion of fat in body. Liver also plays an important role in fat and carbohydrate metabolism.
Symptoms of liver disease
Early or mild form of liver diseases may give rise to non-specific symptoms like fatigue or weakness. Significant liver injury can cause jaundice, which means yellow discoloration of sclera of eye ball and is associated with dark yellow urine. Liver cirrhosis results from persistent damage to liver due to any cause (alcohol, hepatitis B & C). Common manifestations of liver cirrhosis are ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdomen), loss of consciousness (coma) and bleeding from gastrointestinal tract in form of vomiting of blood.
Types of Liver disease
Liver diseases are of two types: (a) Short lasting and self limiting which resolves completely without causing any permanent damage or functional impairment and (b) Smoldering slow diseases which cause a permanent damage to liver which is manifest as “liver cirrhosis”.
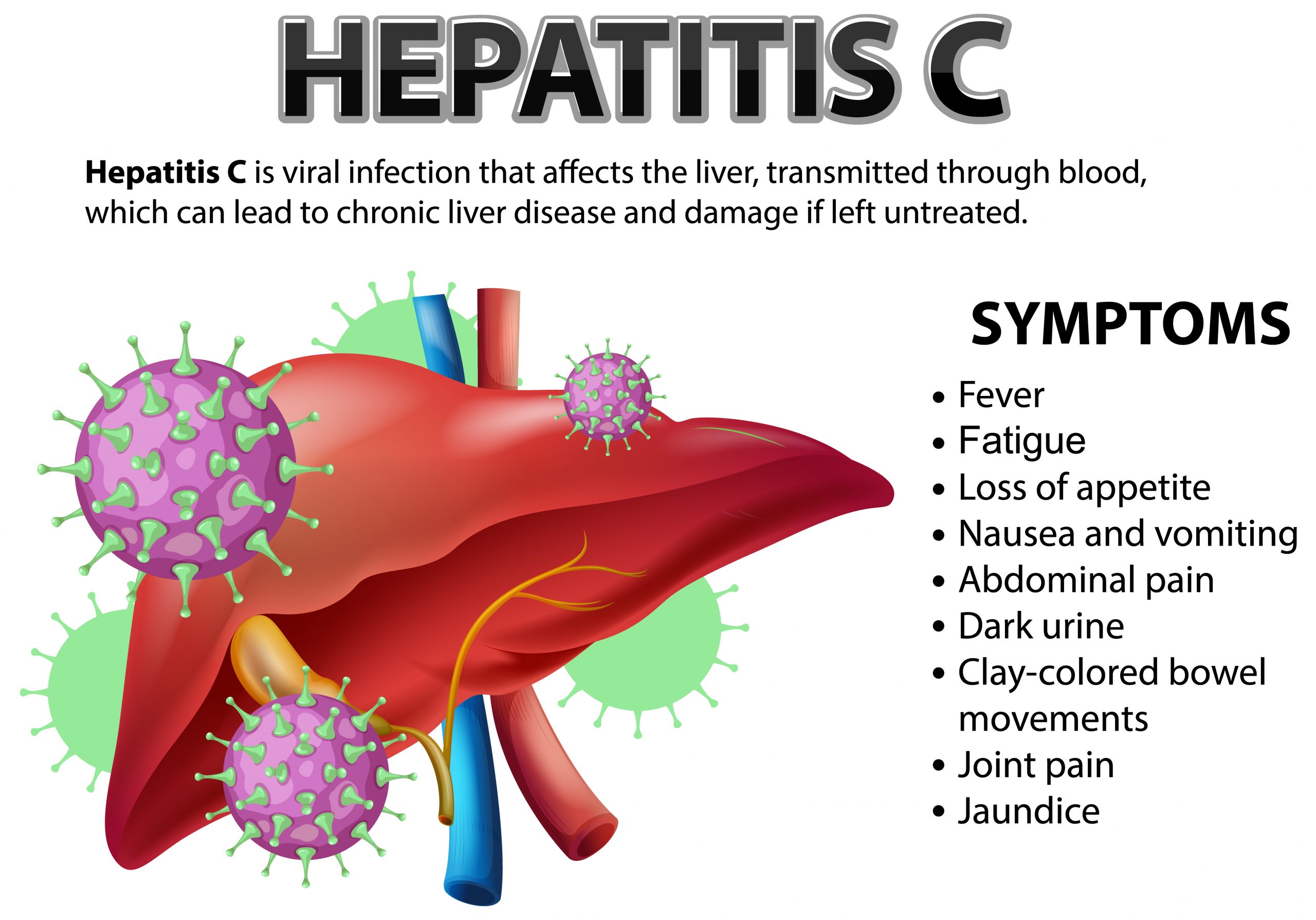
Among the hepatitis viruses, Hepatitis A and E causes jaundice, which is self-limiting. Unlike other types of viral hepatitis, hepatitis A does not cause long-term liver damage, and it does ntt become an ongoing chronic infection. In rare cases, hepatitis A can cause a sudden or acute loss of liver function, especially in older adults or people with chronic liver diseases. Hepatitis A and E are spread by contaminated food and water. Thus if we have safe drinking water supply and pay attention to hygiene these diseases can be prevented. There is vaccine available for hepatitis A and can be used safely at any age. There is no vaccine available for hepatitis E at present but safe drinking water could be the most effective measure to control hepatitis.
Hepatitis B and C cause chronic infection of liver, which can be cause cirrhosis of liver. Hepatitis C is the leading cause of cirrhosis worldwide. In our country hepatitis B is a major challenge. Both hepatitis B and C are spread by blood transfusion, needle sharing, sexual contact and from mother to child. Thus to a large extent these things are preventable by simple measures like improving our testing in blood bank, increasing awareness for voluntary blood donation, educating people against reuse or needle sharing and safe sex practices. In addition we have a very effective vaccine against hepatitis B. There is no vaccine against hepatitis C is as yet. Hepatitis C has a very high prevalence in parts of India where intravenous drug abuse is rampant. Public awareness is the most important tool in preventing the spread of this disease.
Today intake of alcohol has become most socially accepted poison. In ILBS there are over 48 percent of liver disease patients due to high consumption of alcohol. Alcohol is very important cause of liver disease. Alcohol consumption has increased across all social, age and gender groups. Awareness about alcohol consumption is of paramount importance in preventing liver disease. Lack of self help groups and social stigma in approaching them prevents people in need of help from coming out in open. We need a massive public awareness campaign to educate people about safe and responsible alcohol consumption.
Fatty liver is a condition usually picked up incidentally on routine ultrasound and investigation for deranged liver function tests. It is a slowly progressive disease but in a significant number of subjects can lead to liver cirrhosis over years to decades. The most common causes for fatty liver are obesity and diabetes. The epidemic of fatty liver has grown with rise in these lifestyle diseases. In western world it is already the second most common cause of liver cirrhosis after hepatitis C. Prevention remains the cornerstone of treatment of treatment of fatty liver. Adopting a healthy lifestyle with dietary precautions are more effective than medication in early course of this disease.
According to Dr Sarin, fatty liver is the first part of development of other systemic problems. Eating excess calories causes fat to build up in the liver. When the liver does not process and break down fats as it normally should, too much fat will accumulate. People tend to develop fatty liver if they have certain other conditions, such as obesity, diabetes or high triglycerides.
As per report, 1.5 billion people have fatty liver disease in all over the world while in India more than 250 million have fatty liver disease. In India, 1 in 3 has liver disease. Diabetes raises risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. In this condition, fat builds up in liver even if one drinks little or no alcohol. At least half of people living with type 2 diabetes have non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Basically Fatty liver may cause no damage, but sometimes the excess fat leads to inflammation of the liver. When glucose levels are elevated in the context of pre-diabetes or overt diabetes, this provides further substrate for triglyceride synthesis. Additionally, impaired very low density lipoprotein secretion, which commonly occurs with insulin resistance, further contributes to hepatic fat accumulation. Fatty liver disease is a common condition caused by the storage of extra fat in the liver.
Most people have no symptoms, and it does not cause serious problems for them. In some cases, though, it can lead to liver damage. The good news is you can often prevent or even reverse fatty liver disease with lifestyle changes. The most important thing to recognize about liver disease is that up to 72 percent of individuals with underlying liver disease have no symptoms. The most common symptoms are very non-specific and they include fatigue or excessive tiredness, lack of drive, and sometimes itching. It has been seen that obesity and alcohol consumption, which are common and increasing in many parts of the world, have become key liver disease risk factors. Historically, viral hepatitis has been the leading etiology for chronic liver disease. However, improved prevention strategies and treatment have led to improving chronic liver disease trends.

